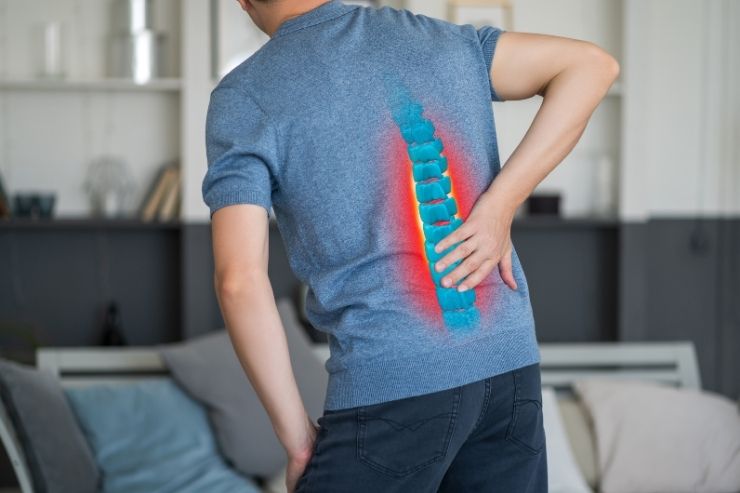
A herniated disc, also known as a slipped or ruptured disc, occurs when one of the discs that cushion the vertebrae in your spine pushes out of its normal position. This can put pressure on the surrounding nerves, leading to pain, numbness, and weakness, often in the back, neck, or legs.
What Causes a Herniated Disc?
Herniated discs are most commonly caused by age-related wear and tear, known as disc degeneration. As you age, the discs in your spine lose some of their water content, making them less flexible and more prone to tearing or rupturing with even a minor strain or twist. Other factors that can contribute to a herniated disc include:
Symptoms of a Herniated Disc
The symptoms of a herniated disc can vary depending on the location of the herniation and the nerves affected. Common signs include:
Managing and Treating Herniated Discs
Treatment for a herniated disc often starts with conservative measures, and surgery is usually considered only when these options do not provide relief.
Surgical Options
If conservative treatments fail, or if there is significant nerve compression, surgery may be necessary. Common surgical options include: