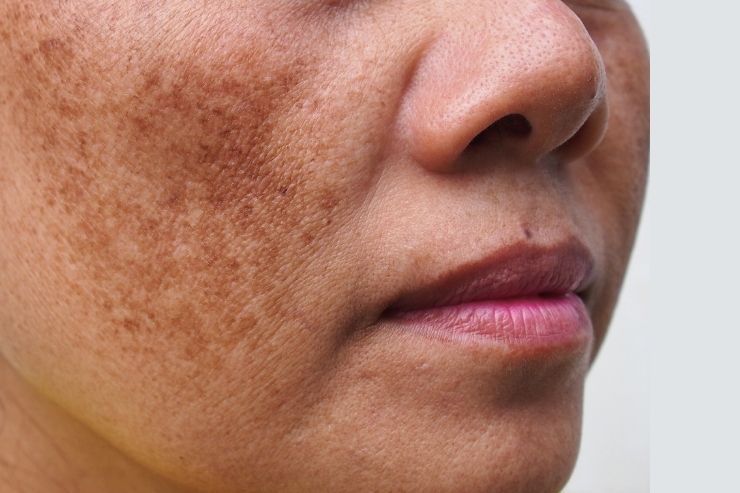
Melasma is a common skin condition characterized by dark, discolored patches on the skin, typically on the face. Often referred to as the “mask of pregnancy” when it occurs in pregnant women, melasma can affect anyone and is particularly prevalent among those with darker skin tones. At PARI HOSPITAL, our dermatology experts specialize in diagnosing and treating melasma to help patients achieve clearer, more even-toned skin.
What is Melasma?
Melasma is a form of hyperpigmentation that usually appears as brown or gray-brown patches on the face. It most commonly affects the cheeks, forehead, bridge of the nose, upper lip, and chin. Although melasma is not harmful, it can be a cosmetic concern for many people.
Melasma is primarily caused by an overproduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Several factors can trigger this overproduction, including:
Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, especially during pregnancy, can trigger melasma. It is also commonly associated with the use of oral contraceptives and hormone replacement therapy.
Sun Exposure: Ultraviolet (UV) light from the sun is a significant trigger for melasma. UV exposure can stimulate melanocytes, the cells that produce melanin, leading to the development or worsening of melasma.
Genetics: A family history of melasma increases the likelihood of developing the condition. Individuals with a genetic predisposition to melasma are more prone to experiencing it.
Skin Care Products: Certain skin care products or procedures that irritate the skin can trigger melasma, particularly if they cause inflammation or sensitivity.
Medications: Some medications, particularly those that make the skin more sensitive to sunlight, can contribute to the development of melasma.
Symptoms of Melasma
Melasma typically presents as symmetrical patches of discoloration on the face, although it can occasionally appear on other sun-exposed areas of the body, such as the neck or forearms. The patches are usually:
Brown or Gray-Brown in Color: The pigmentation can range from light to dark brown or even blue-gray, depending on the depth of the pigment in the skin.
Symmetrical: The patches often appear on both sides of the face, making them symmetrical.
Irregular in Shape: Melasma patches are often irregular in shape, with well-defined borders.
Treatment Options for Melasma
While melasma can be persistent, effective treatments are available at PARI HOSPITAL to help reduce the appearance of dark patches and prevent further pigmentation:
Topical Medications: Prescription creams containing hydroquinone, tretinoin, corticosteroids, or a combination of these can lighten the dark patches over time.
Chemical Peels: Light chemical peels using glycolic acid or other agents can help exfoliate the skin, promoting the shedding of pigmented cells and revealing clearer skin underneath.
Laser and Light Therapies: Advanced laser treatments and intense pulsed light (IPL) therapy can target and break down excess melanin in the skin, reducing the appearance of melasma.
Microneedling: This minimally invasive procedure stimulates collagen production and can help reduce hyperpigmentation by improving skin texture and tone.
Sun Protection: Strict sun protection is crucial in managing melasma. Daily use of broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding direct sun exposure can help prevent the worsening of melasma.
Skin Lightening Agents: In addition to hydroquinone, other skin lightening agents like azelaic acid, kojic acid, and vitamin C can be used to treat melasma.