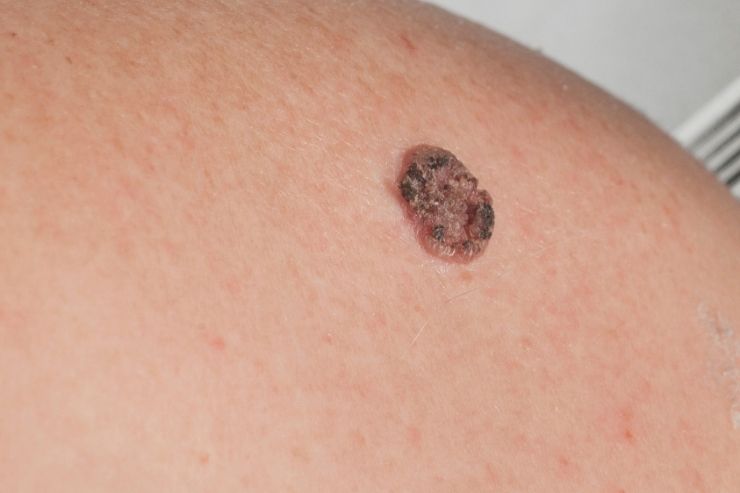
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC) is a common type of skin cancer that originates in the squamous cells, which are thin, flat cells found in the outer layer of the skin (epidermis). It can also develop in other areas lined with squamous cells, such as the mouth, throat, and lungs. Early detection and treatment are crucial for effective management and positive outcomes.
What is Squamous Cell Carcinoma?
Squamous Cell Carcinoma is characterized by the abnormal growth of squamous cells. These cancerous cells can invade surrounding tissues and may spread to other parts of the body if not treated promptly.
Key Features of SCC:
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing Squamous Cell Carcinoma:
Symptoms of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The symptoms of SCC can vary, but common signs include: