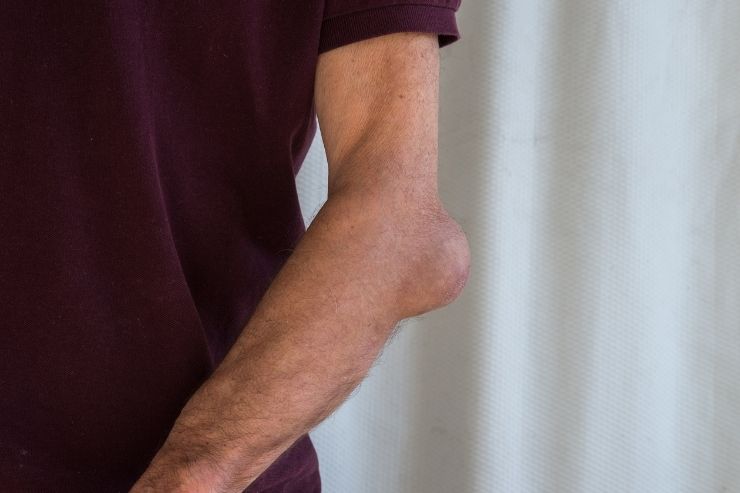
Bursitis is an inflammation of the bursa, a small, fluid-filled sac that acts as a cushion between bones and soft tissues, such as muscles, tendons, and skin. Bursae are located throughout the body, particularly in areas where friction occurs, such as the shoulders, elbows, hips, and knees. When these sacs become inflamed, it can lead to pain, swelling, and reduced movement in the affected area.
Causes of Bursitis
Bursitis typically results from irritation or injury to the bursa. Common causes include:
Symptoms of Bursitis
The symptoms of bursitis can vary depending on the location and severity of the inflammation but generally include:
Diagnosis of Bursitis
To diagnose bursitis, a healthcare provider will typically:
Treatment Options for Bursitis
Treatment for bursitis aims to reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and restore function. Common approaches include:
Prevention of Bursitis
To prevent bursitis, consider the following strategies: